Approximately one third of the top 200 prescribed drugs which undergo drug metabolism are substrates for metabolic clearance mediated by enzymes other than CYPs. The most prevalent are UDP-glucuronosyl transferases and esterases accounting for approximately 8% and 5% of the metabolized drugs respectively1,2. Numerous other more minor pathways exist including: flavin monooxygenases (FMO), monoamine oxidases (MAO), aldehyde oxidases (AO), aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH), aldo-keto reductases (AKR), alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) and hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (HSD), sulphotransferases (SULT), N-acetyltransferases (NAT) and glutathione S-transferases (GST). Both the EMA3 and FDA4 guidance on drug interactions suggest that both CYP and non-CYP pathways should be elucidated if thought to contribute a significant amount to drug elimination.
Evotec, and wholly owned subsidiary Cyprotex, provide a full range of drug metabolism service for determining metabolic stability and potential drug-drug interactions for CYP and non-CYP mediated metabolism. Our experienced team can provide support from early stage screening assays to late stage regulatory packages.
Non-CYP Mediated Metabolism Services
Our non-CYP metabolism service enables a greater understanding of which non-CYP enzymes might be involved in the metabolism of your compounds, or if your compounds are inhibitors of non-CYP enzymes. These data can be used to determine potential drug-drug interactions.
Reaction Phenotyping
In order to determine which CYP and non-CYP enzymes are involved in the metabolism of a compound, reaction phenotyping studies are recommended in early development. This information is useful for predicting possible drug-drug interactions with co-administered therapies, and in identifying whether polymorphic enzymes play a significant role in the drug metabolism.
Available reaction phenotyping services include:
- Phase I:
- Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP)
- Flavin monooxygenases (FMO)
- Monoamine oxidases (MAO)
- Esterases, including carboxylesterases (CEs), cholinesterases (acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)) and paraoxonase (PON)
- Aldehyde oxidase (AO)
- Aldo-keto reductases (AKR)
- Phase II:
- UDP-glucuronyltransferases (UGT)
- N-Acetyltransferases (NAT)
Bespoke assays can be designed based on customer’s specific
requirements to evaluate potential non-CYP mediated metabolism. Our specialists can advise on different options regarding the test
systems available (i.e. recombinant enzymes preparations or metabolism
in microsomes, cytosol or plasma (plus and minus different inhibitors)).
Please contact us to find out more about our custom non-CYP mediated metabolism services.
Enzyme Inhibition Studies
Understanding whether a compound can inhibit drug metabolizing
enzymes is important in establishing its drug interaction potential.
Also, in some circumstances inhibition of an enzyme may be a critical
mechanism of action for a drug (e.g., monoamine oxidase inhibitors in
the treatment of Parkinson’s disease).
Available enzyme inhibition services include:
- Phase II:
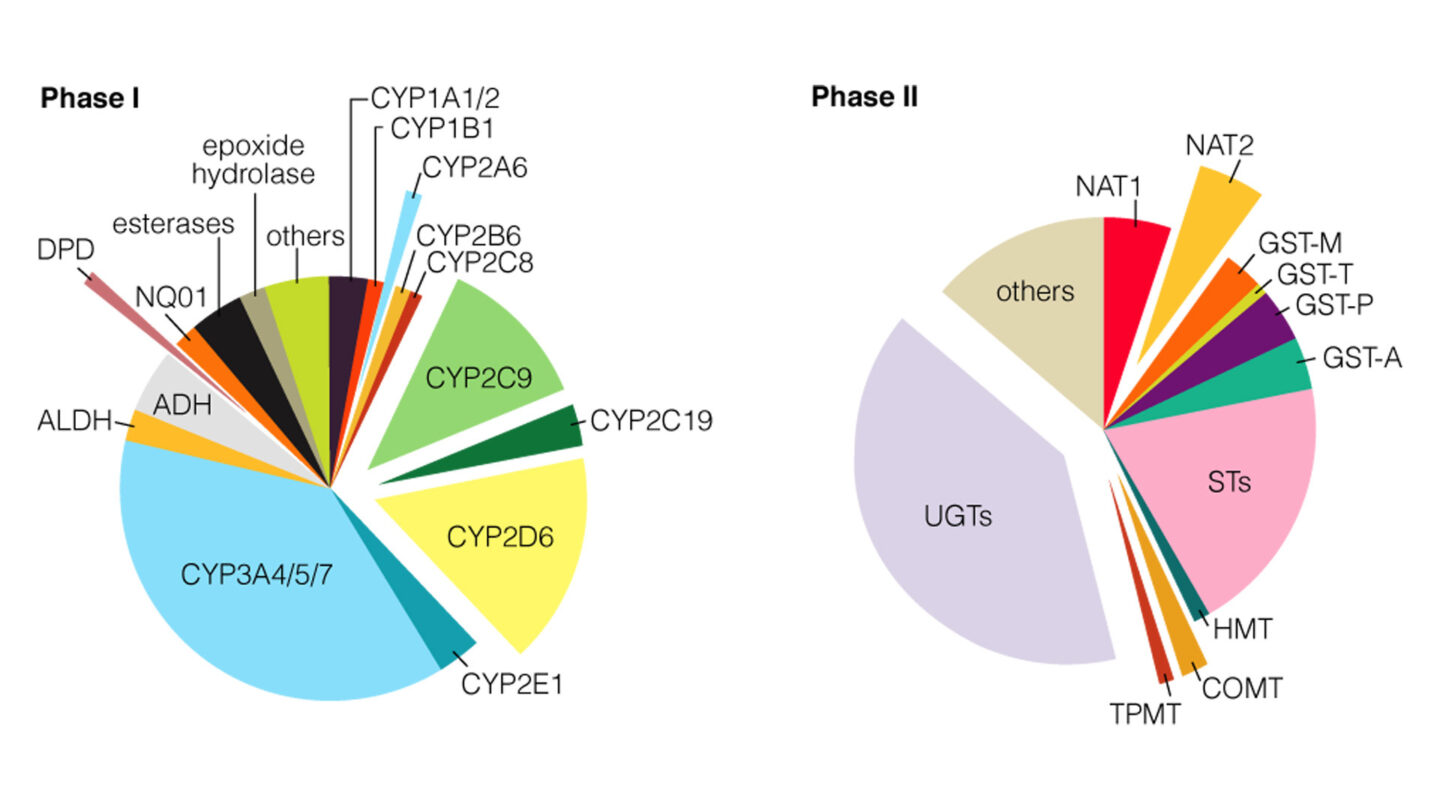
Figure 1
The percentage of Phase I and II metabolism that each enzyme contributes correlates with the estimated relative size of the corresponding pie chart5.
(From Evans and Relling (1999). Pharmacogenomics: Translating functional genomics into rational therapeutics. Science, 286, 487-4915)
The non-CYP mediated metabolism services described above expand the offering of Cyprotex’s existing drug metabolism assays:
- Metabolic stability (microsomes, hepatocytes, S9, plasma)
- Reversible CYP450 Inhibition
- CYP450 Time Dependent Inhibition (IC50 shift and kinact/KI)
- CYP450 Induction
- Relative Induction Score
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
References
1) Williams JA, et al., (2004) Drug-drug interactions for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates: a pharmacokinetic explanation for typically observed low exposure (AUCI/AUC) ratios. DMD 32; 1201-1208
2) Beaumont K et al., (2010) ADMET for the medicinal chemist. In RCS Drug Discovery Series No. 1: Metabolism, Pharmacokinetics, and Toxicity of Functional Groups: Impact of Chemical Building Blocks on ADMET. Edited by Smith DA; 61-98
3) The European Medicines Agency (EMA) Guideline on the Investigation of Drug Interactions (Adopted 2012)
4) FDA Guidance for Industry – In Vitro Drug Interaction Studies - Cytochrome P450 Enzyme- and Transporter-Mediated Drug Interactions (January 2020)
5) Evans WE and Relling MV (1999) Pharmacogenomics: Translating functional genomics into rational therapeutics. Science 286; 487-491
* Reprinted with permission from AAA. Readers may view, browse, and/or download material for temporary copying purposes only, provided these uses are for noncommercial personal purposes. Except as provided by law, this material may not be further reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, adapted, performed, displayed, published, or sold in whole or in part, without prior written permission from the publisher.